In the realm of health, heart wellness has always been a focal point. Today, we present the “invisible guardian” of cardiac health: NT-proBNP.
Also known as N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, NT-proBNP acts as the heart's 'little sentinel', serving as a key indicator of cardiac function. When the heart is under stress, such as an increased workload or myocardial damage, heart muscle cells release a substance called BNP, which simultaneously produces NT-proBNP. The greater the stress on the heart, the higher the concentration of NT-proBNP in the blood.
Core Clinical Value of
NT-proBNP
NT-proBNP is highly valuable for the clinical diagnosis, risk stratification, assessment of prognosis, and monitoring of treatment in patients with acute (AHF) and chronic (CHF) heart failure. The 2014 Chinese Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Heart Failure (hereafter referred to as the 'Guidelines') state that NT-proBNP assists with the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of AHF (Grade I, Class A recommendation). An NT-proBNP level of less than 300 pg/ml is recommended as the cut-off point for ruling out AHF. The Guidelines also recommend stratification based on age and renal impairment. Cutoff values for confirming AHF are >450 pg/ml for adults under 50 years old, >900 pg/ml for those aged 50–75 years, >1,800 pg/ml for individuals over 75 years old and >1,200 pg/ml in cases of renal impairment. Specifically, an NT-proBNP level of >10,000 pg/ml indicates probable severe AHF requiring hospitalisation for close monitoring. Patients with NT-proBNP levels between 300 and their age-specific cutoff level are in a 'grey zone' where diagnosis is uncertain. These cases require an appropriate clinical diagnosis and treatment based on symptoms. Professor Zhang Yuhui emphasised: 'Beyond aiding AHF diagnosis, NT-proBNP monitoring during hospitalisation reflects treatment efficacy and prognosis. Post-treatment, persistently elevated NT-proBNP levels or failure to decrease by more than 30% indicate a poor response, increasing the risk of readmission and mortality. Conversely, sustained low NT-proBNP levels or reductions exceeding 30% indicate a favourable response to treatment and prognosis." NT-proBNP also correlates positively with CHF severity. The guidelines recommend routine NT-proBNP testing for patients with CHF to diagnose and differentiate cases of suspected heart failure presenting with dyspnoea, as well as to assess CHF severity and prognosis (Class I, Level A recommendation). A 2008 study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (J Am Coll Cardiol) enrolled 1,618 heart failure patients and demonstrated that monitoring NT-proBNP levels over time aids in assessing CHF prognosis. Patients with persistently low NT-proBNP levels, or who experienced a decrease from high to low levels, had significantly lower mortality and heart failure hospitalisation rates than those with persistently high levels, or who experienced an increase from low to high levels. Additionally, NT-proBNP levels exceeding 1000 pg/mL indicate a poor prognosis and represent an appropriate threshold for assessing long-term patient outcomes clinically.
Rapid Testing, Efficient Care
So, what is the purpose of NT-proBNP testing? It is a valuable tool that helps doctors diagnose and treat heart conditions. In terms of diagnosis, it enables physicians to quickly determine whether a patient has heart failure. When patients present with symptoms such as shortness of breath, measuring NT-proBNP levels can provide strong evidence of heart failure if the values are significantly elevated. Moreover, it can help to determine whether shortness of breath is caused by the heart or by other factors, thus enhancing diagnostic accuracy. NT-proBNP also plays a crucial role during treatment. Doctors can monitor numerical changes to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. If treatment is effective and cardiac function improves, NT-proBNP levels will decrease progressively. Conversely, persistently high or rising levels suggest that the treatment plan may require adjustment.
Measuring NT-proBNP is extremely convenient as it only requires a small sample of venous blood. Results are available quickly, saving valuable time for diagnosing and treating patients. NT-proBNP acts as a guardian of heart health, silently safeguarding our well-being.
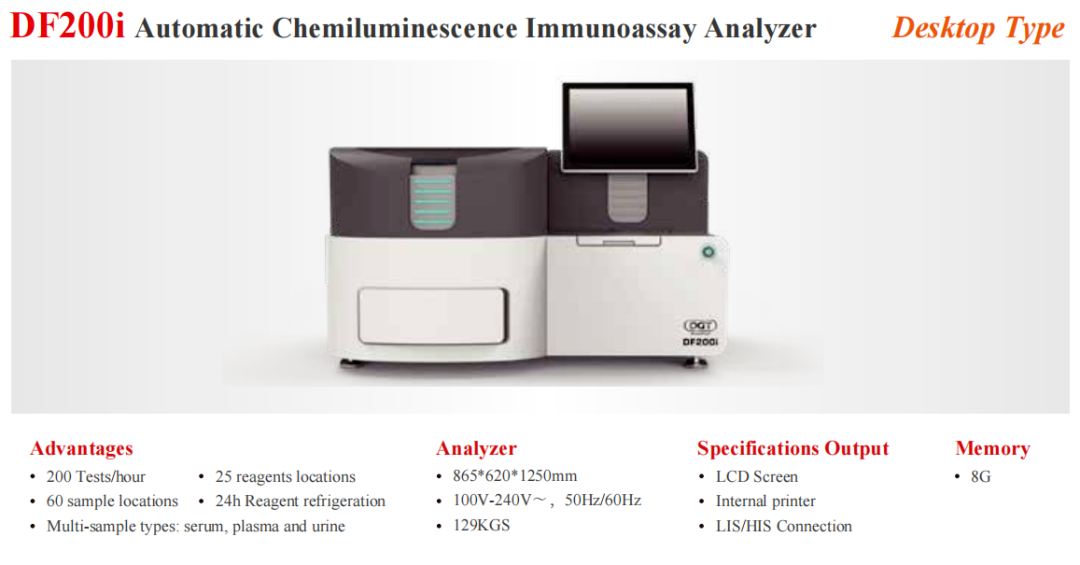
Automated Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Platformfor Chemicals and Biologics