The present study enrolled 11 patients treated for ventriculitis. However, two of these patients were ultimately excluded due to the retrieve of other sources of infections, leading to frequent change of antibiotics, and only 9 patients were retained. In the trial, the first serum and cerebrospinal fluid concentration tests were performed 24 hours after initiation of dosing, and dose adjustments were made at the 48-hour time point. This was followed by a second drug concentration test at 72 hours, followed by dose adjustment at the 96-hour time point. As shown in Figure 1.
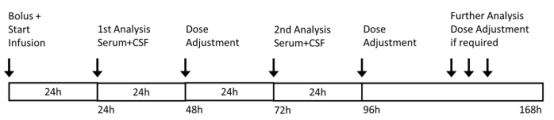
Figure 1 Treatment regimen. Serum and CSF concentrations were analyzed after 24 and 72 h with consecutive dose adjustment after 48 or 96 h from the start of infusion. Further analysis and dose adjustment were only performed where necessary.
The median values of the initial dose for 9 patients were 8.8 g of meropenem and 4.25 g of vancomycin, which equals 114.3 mg/kg bodyweight/24h meropenem and 57.2 mg/kg of bodyweight/24h vancomycin respectively. It is noteworthy that no renal impairment could be detected despite high-dose vancomycin therapy. Dose adjustments after 48h were made in four of the patients (three reduced the dose of both drugs and one reduced the therapeutic dose of vancomycin only) according to the results of serum TDM. After the second TDM analysis, another 4 patients underwent dose adjustments, of which the dose was enhanced for 1 patient. After dose adjustment, final cerebrospinal fluid blood levels reached the target values in all 9 patients.
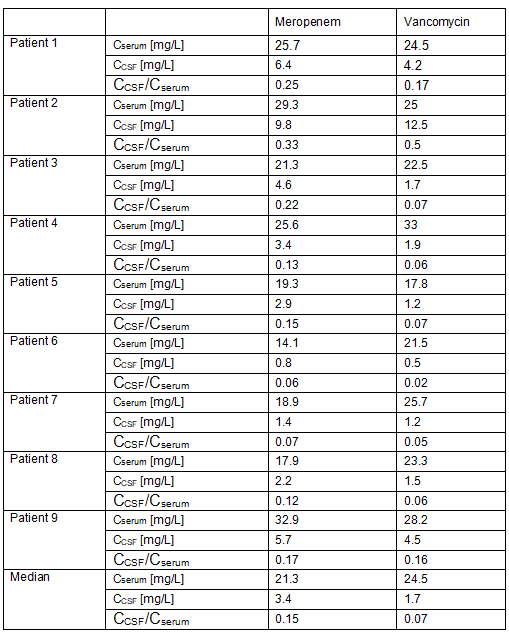
As seen in the comparison of serum and cerebrospinal fluid data based on TDM, respectively, the median value of the CCSF/Cserum ratio for meropenem was 0.15 (0.06; 0.33), and the median value of the CCSF/Cserum ratio for vancomycin was 0.07 (0.02; 0.50). As shown in Table 1, vancomycin cerebrospinal fluid concentrations were more variable than meropenem. However, two of the patients (#6, #7) had low CCSF/Cserum ratios and resulted in insufficient CSF concentrations, whereas vancomycin had low CSF concentrations in only one case (patient #6).
Table 1. Serum and CSF concentration in each patient 24h after infusion start.