Aminoglycoside antibiotics:
therapeutic tools
Aminoglycoside antibiotics (AmAn) are stationary-phase bactericidal drugs that can bind to the 30S subunit in bacterial ribosomes to inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. They can also change the permeability of bacterial cell walls, allowing intracellular salts and Nutrients leak out, causing bacteria to die quickly. It is mainly used clinically for severe systemic infections caused by aerobic Gram-negative bacilli, including biliary tract infections, bone and joint infections, urinary tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, etc.
AmAn has high polarity and dissociation, and is difficult to absorb when taken orally. In clinical practice, intramuscular injection and intravenous infusion are the main methods. After repeated administration, it is easy to accumulate in high concentrations in the renal cortex and inner and outer lymphatic fluid of the inner ear.
AmAn has the characteristics of narrow therapeutic window, prone to adverse reactions and large individual differences. In particular, regular TDM is needed to improve medication safety and reduce the incidence of ototoxicity and renal toxicity.
Factors such as gender, age, race, and burn injuries will all affect the patient's apparent volume of distribution, thereby affecting the blood concentration of AmAn.
AmAn drugs is close to the toxic concentration. There is a large difference in the blood drug concentration in patients after the same dose of drugs is given, which affects the efficacy of the drug and even causes toxic reactions, especially in special populations.
The "Guiding Principles for Clinical Application of Antimicrobial Drugs" stipulates that patients with renal insufficiency, the elderly, and newborns who use aminoglycosides need to undergo TDM to improve efficacy and reduce adverse reactions. Patients with abnormal renal function should measure Cmax on the 2nd day after medication (5 minutes after medication); measure Cmin on the 4th to 5th day of medication (5 minutes before medication), and use TDM to guide clinical rational drug use to avoid excessive concentrations and cause toxic reactions.
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
Safeguard
Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is a technology that detects the concentration of drugs and related metabolites in biological samples. Guided by the basic theories of pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD), analytical technology is used to detect the drug concentration in the patient's body and evaluate whether the patient's dosage regimen is appropriate to improve efficacy and reduce the occurrence of toxic reactions. For AmAn, which has a narrow therapeutic window, is prone to adverse reactions and has large individual differences, regular TDM is particularly necessary to improve medication safety, reduce the incidence of ototoxicity and renal toxicity, and improve clinical medication from the traditional empirical model to the level of precision medication.
This type of antibiotics has a long post-antibiotic effect and first-dose effect, and is a concentration-dependent antibiotic. The clinical efficacy is positively related to the ratio of peak concentration (Cmax)/minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). When Cmax/MIC≥8-10, or when the area under the drug-time curve (AUC)/MIC ≥ 100-125, good efficacy can be achieved against Gram-negative bacteria , and it can also prevent the generation of drug-resistant mutant strains during the treatment process.
Optimization of dosing regimen
The clinical use of AmAn often requires the formulation of individualized dosing regimens based on TDM based on empirical dosing regimens (see the table below for conventional dosing doses) to improve clinical cure rates and reduce antibiotic resistance.
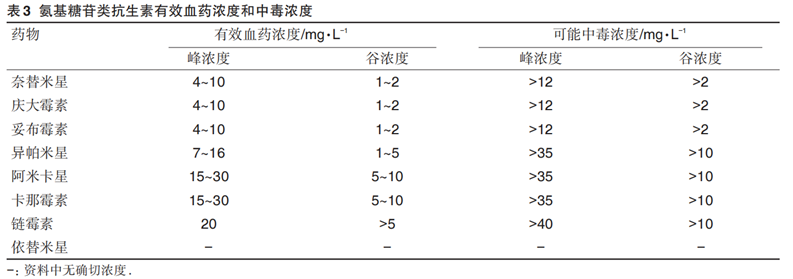
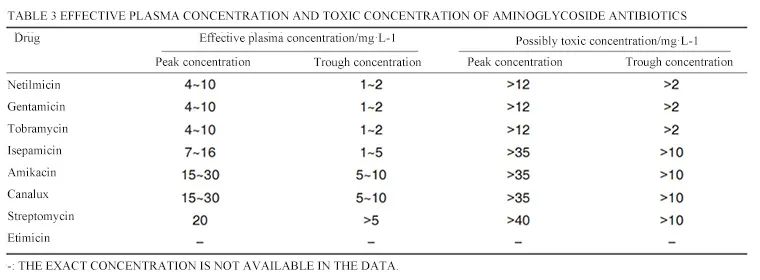
However, the therapeutic concentration of AmAn is close to the toxic concentration, and toxic reactions are prone to occur. Special attention needs to be paid to the peak and trough concentration values when using it. The specific values of therapeutic concentrations and toxic doses of this type of antibiotics are shown in the table below.
Progress in research on
toxicological mechanisms
After studying the nephrotoxicity of AmAn, it was found that first, the drug was absorbed by proximal tubule cells through pinocytosis and then transported and accumulated on lysosomes, leading to denaturation of lysosomal phospholipids, lysosome rupture, and phospholipiduria. This can lead to renal tubular cell necrosis and even renal failure.
The main mechanisms may be:
① AmAn induces oxidative stress and leads to kidney damage. For example, amikacin and gentamicin can significantly reduce the SOD activity of the human renal tubular epithelial cell line HK-2, increase the content of MDA and lactate dehydrogenase, and cause toxicity;
② AmAn induces apoptosis and necrosis of normal cells, leading to kidney damage. For example, gentamicin and etimicin can increase interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-α, (TNF-α) in rats and other pro-inflammatory factors, leading to apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells.
In response to AmAn nephrotoxicity, researchers propose that the following protective measures can be taken clinically:
① Adopt a once-daily administration regimen to reduce absorption by reducing pinocytosis;
② Avoid local or systemic combination with other nephrotoxic drugs;
③ Change the route of administration and study antibiotics with lower toxicity. Nebulized aminoglycosides have been used to treat COPD;
④Combined with drugs to reduce nephrotoxicity. For example, dexamethasone and tacrolimus can alleviate oxidative stress cell damage caused by gentamicin metabolites.
In summary, it is extremely necessary to perform TDM on AmAn. Developing an individualized dosage regimen through TDM can effectively reduce its ototoxicity and renal toxicity and drug resistance, and improve the patient's cure rate.
Diagreat product solutions
Based on the chemiluminescence platform, Diagreat Biotech provides multiple series of blood drug concentration monitoring packages for anti-infectious drugs, immunosuppressive drugs, antipsychotic drugs, anti-tumor drugs, cardiac glycoside drugs, antiasthmatic drugs, etc. (see table below). Among them,the combination of "gentamicin + tacrolimus" can reduce renal toxicity and has certain clinical value in reducing toxic and side effects (see above). Diagreat chemiluminescence detection instruments have the characteristics of high degree of automation, fast testing speed, large detection throughput, stable operation, superior performance, and perfect traceability, etc., and can provide complete solutions for users at different levels.