The patient in this case is a 40-year-old woman who is 29 weeks pregnant. The fetus is grossly normal, with an estimated fetal weight of 1,671 g; however, electronic fetal heart rate (FHR) monitoring revealed cardiomegaly and FHR of > 200 beats per minute (bpm). Fetal echocardiography in M-mode revealed an atrial rate of up to 500 bpm and a ventricular rate of 228–236 bpm (A:V ratio of 2:1).
Transplacental digoxin therapy was planned to control the fetal rate. The initial dose of digoxin in the first 20 minutes is 0.6 mg intravenously, followed by 0.3 mg every 8 hours. To ensure the safety and efficacy of the treatment, TDM of digoxin in maternal serum was conducted. The observed digoxin concentrations were 0.67, 0.83 and 1.05 ng/ml on the first, second and fifth days respectively. In the fifth day of treatment, the serum level of digoxin had reached the target range while the FT duration increased. Digoxin dosage was discontinued, and was replaced with oral flecainide in the sixth day. FHR fell into the normal range within 2 days of treatment changing. Until the final cesarean delivery, no any symptoms were observed in either the patient and fetus. The whole treatment period lasted around 9 weeks.
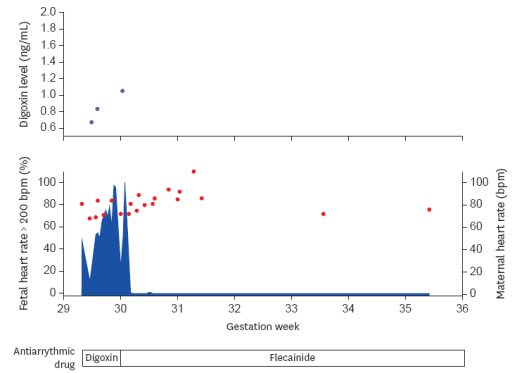
Figure 1. Treatment of digoxin and flecainide, the concentration of digoxin, percentage of fetal heart rate > 200 bpm (blue filled area, left y-axis) and maternal heart rate (red circle, right y-axis). The patient was hospitalized at hospital from 29 weeks of gestation and delivered at 38 weeks and 1 day of gestation.