The use of monoclonal antibodies to recognize D-dimer epitopes in whole blood or plasma is the basic principle of D-dimer detection. Currently, the commercial D-dimer detection methods commonly used in clinical practice mainly include the following four types: whole blood agglutination detection method, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay or enzyme-linked fluorescent assay, l latex enhanced immunoturbidimetric assay, and chemiluminescence method.
Table 1 Characteristics of different detection methods for D-dimer
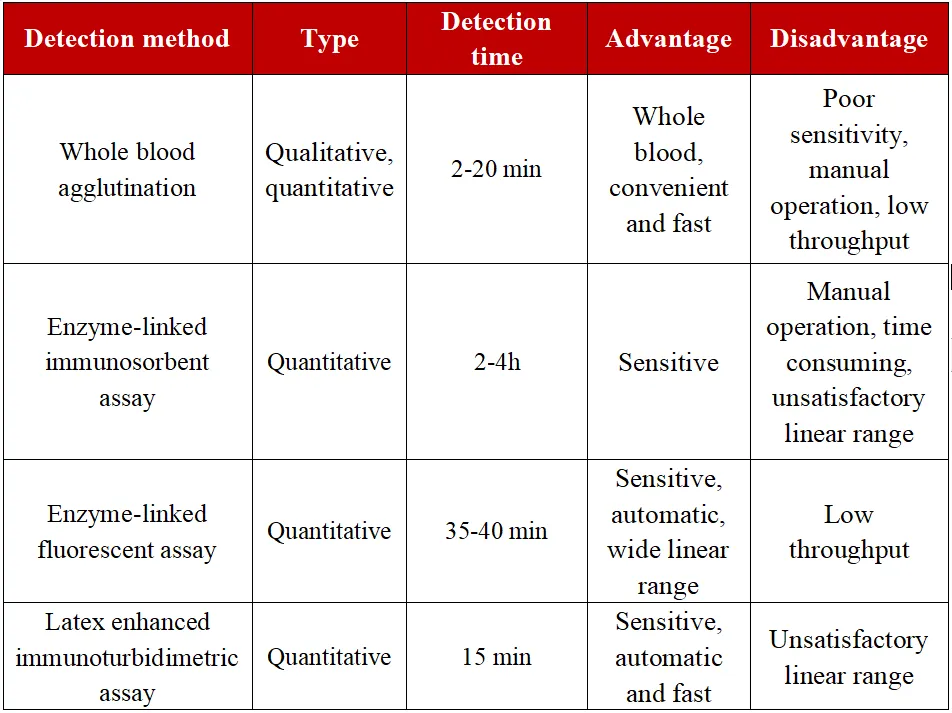
The monoclonal antibodies selected by different kits have inconsistent affinity for the D-dimer in the mixed fragments, and the calibrator system cannot be traced. Therefore, it is recommended that the same medical institution should use the same D-dimer detection method and the same detection system, and test workers should be familiar with the D-dimer detection method, detection sensitivity and negative predictive value of the laboratory (highly recommended).
Sample factors, physiological state, and drug effects should always be considered when interpreting D-dimer test result (highly recommended).
The elements that should be provided in the D-dimer report include: normal reference interval, cut off value for venous thromboembolism (VTE) exclusion diagnosis (if verified), reporting method (FEU or DDU) and measurement unit (μg/L, mg/ L) (strongly recommended).