To evaluate the importance of peak and trough VCM concentrations, subjects in the TDM group were divided into two groups based on peak concentrations:TDM group A, with peak concentrations higher than 25 mg/mL (n=529), and TDM group B, with peak concentrations lower than 25 mg/mL (n=524), to study the relationship between serum VCM concentrations and the duration of VCM treatment in the two groups of patients.
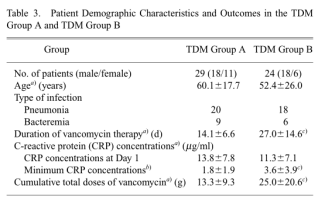
Table 3 Characteristics and outcomes of patients in the TDM and non-TDM groups (Group A: peak vancomycin concentration > 25 mg/mL; Group B: peak vancomycin concentration < 25 mg/mL
The results showed that there was no significant difference in the initial CRP concentration (day 1) between the two groups of patients. the mean duration of VCM treatment was 13 d shorter in group A than in group B (p<0.05); the mean cumulative total dose of VCM in group A was approximately 12 g less than that in group B (p<0.05); and the lowest CRP concentration measured in group A was 1.8 mg/mL lower than that in group B (p<0.05), and by adjusting the peak VCM concentration , clinical outcomes in MRSA-infected patients with pneumonia or bacteremia could be improved.
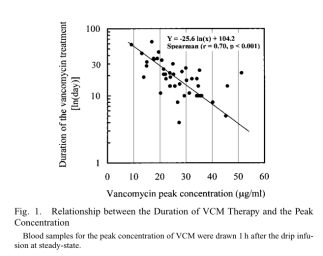
Spearman's correlation analysis showed a significant correlation between peak concentration and duration of VCM treatment (r=0.51, p< 0.01). Treatment duration varied widely among patients with peak concentrations below 25 mg/mL. The time to bacterial disappearance at the site of infection exceeded 30 d in some patients, whereas the time to bacterial disappearance was mostly less than 30 d in patients with peak concentrations above 25 mg/mL. When the peak VCM concentration was above 25 mg/mL, the treatment duration was significantly shorter in patients with MRSA-infected pneumonia or bacteremia.